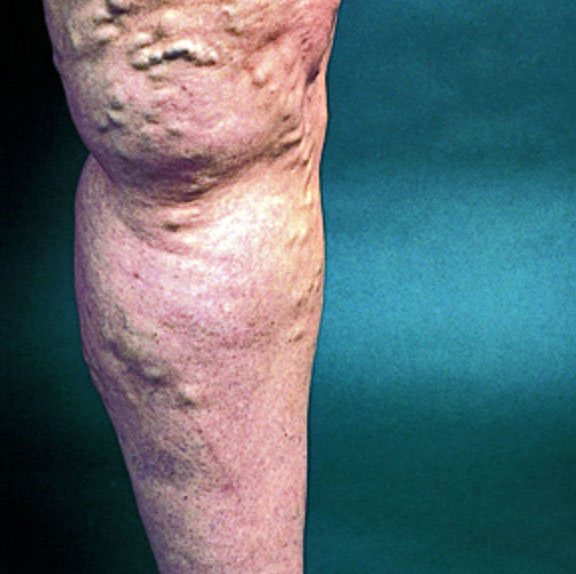
Varicose Veins
Patrizia Grob, OMS III
Varicose veins are abnormally enlarged blood vessels due to faulty valves in your veins. While this is not a serious condition, many people find varicose veins uncomfortable and not aesthetically pleasing to look at. Veins normally have one-way valves that prevent blood from flowing backwards. When these become faulty this
results in blood flowing backwards and pooling, most commonly in the legs.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins: A lot of people do not have any symptoms
Risk Factors and Causes of Varicose Veins:
Treatment:
Go Back results in blood flowing backwards and pooling, most commonly in the legs.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins: A lot of people do not have any symptoms
- Leg pain
- Itching
- Soreness
- Swelling in legs
- Heaviness
- Cramping
- Discoloration of the skin
Risk Factors and Causes of Varicose Veins:
- Family history
- Pregnancy
- Obesity
- Age
- Sitting or standing in one place for a long period of time
- Previous blood clot
Treatment:
- Before treating varicose veins you will get a full workup including an ultrasound of your veins to assess the blood flow in your legs. This will determine what kind of treatment is best suited for you
- Conservative treatment includes compression socks, weight loss, elevating legs, and exercising.
- After trying conservative treatment options next line are minimally invasive procedures, which are usually done in the office as an outpatient. These include venous ablation (sealing off the veins that had bad valves using laser or radio waves) and removing the varicose veins directly through tiny incisions that can be closed with a bandaid.
- If you have varicose veins that are CAUSING SYMPTOMS, ask to see a vascular surgeon. Almost all insurance plans cover symptomatic varicose veins. Treating varicose veins for cosmetic reasons is usually not covered and the results of treatment is usually not worth doing it.