Carotid Artery Disease
Located on each side of the neck, the carotid arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart and to the brain. Carotid Artery Disease is a disease in which plaque builds up in your carotid artery, causing a narrowing (carotid stenosis) or blockage. When this occurs, small clots may form, break off and travel to the brain leading to temporary stroke symptoms (transient ischemic attack or TIA) or a major stroke.
- Up to 3% of individuals older than 65 have carotid artery disease. (Society for Vascular Surgery)
- Carotid Stenosis is responsible for up to one-third of all strokes. Stroke causes 1 in every 15 deaths. About 700,000 strokes occur every year, usually in men. (Society for Vascular Surgery)
Signs and Symptoms
- Brief episode of vision loss in one eye
- Brief episode of weakness on one side of your body
- Brief episode of slurred speech or inability to get words out
- May not have symptoms until a stroke
- Your physician may hear an unusual sound or bruit by stethoscope when listening to your neck
Risk Factors
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure or hypertension
- High cholesterol
- Heart disease
- Aneurysm
- Prior vascular bypass
Detection
A painless, non-invasive ultrasound will diagnose carotid artery narrowing.
Treatment Options
Mild carotid narrowing without any symptoms can be followed by ultrasounds every 6 to 12 months. Medical management by controlling risk factors for hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis) and stroke (i.e. smoking cessation, regular exercise, maintaining healthy blood pressure, excellent control of diabetes, lowering elevated cholesterol and maintaining a normal weight) can slow or stop the progression of plaque buildup. Your physician will likely recommend an aspirin a day or another antiplatelet medication.
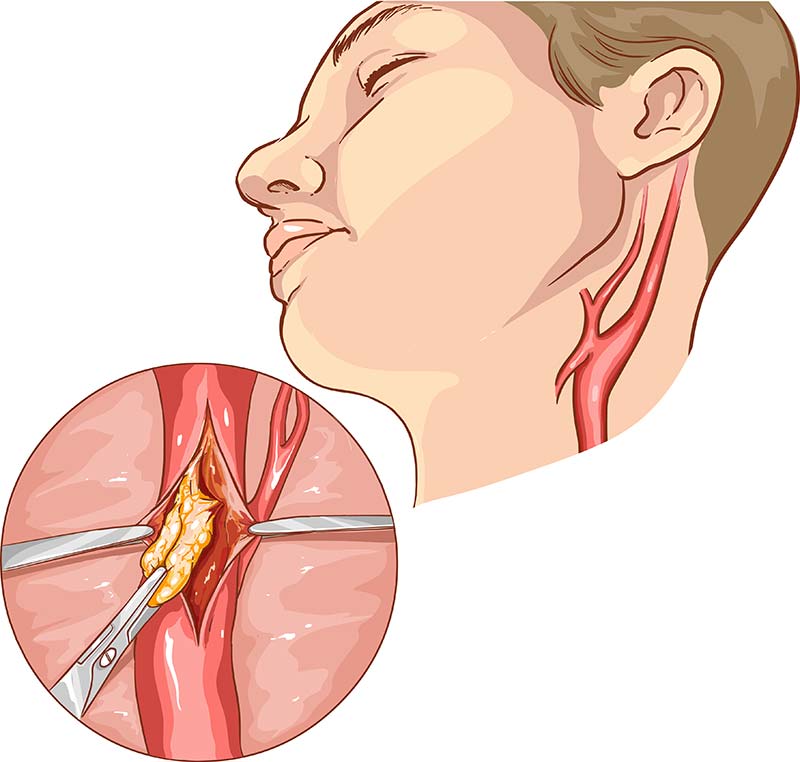
More severe narrowing (>70%), or patients with symptoms as a result of the narrowing, will be evaluated for an intervention to prevent major stroke. Depending on the circumstances, this may be done with either carotid endarterectomy or a carotid stent. With endarterectomy, an incision will be made on the side of the neck. The artery is opened and the plaque removed. The opening in the artery is then stitched closed. The operation takes about 2 hours, and most patients go home the next day. Carotid stent may be also be used in certain circumstances where a metal frame or stent is placed in the artery through a small poke hole in the groin. This also takes about two hours, and patients usually go home the next day.
Call To Schedule An Appointment
303-539-0736