Lower Extremity Chronic Venous Disease
By Dr. Bryan Kramer, MD and Grace Boyle, OMS-II - December 30, 2019
Definition: spectrum of lower extremity vein abnormalities that may be morphologic and/or functional in nature that lead to venous dilation
Go Back - May or may not be symptomatic
- Inadequate muscle pumps
- Incompetent venous valves (reflux)
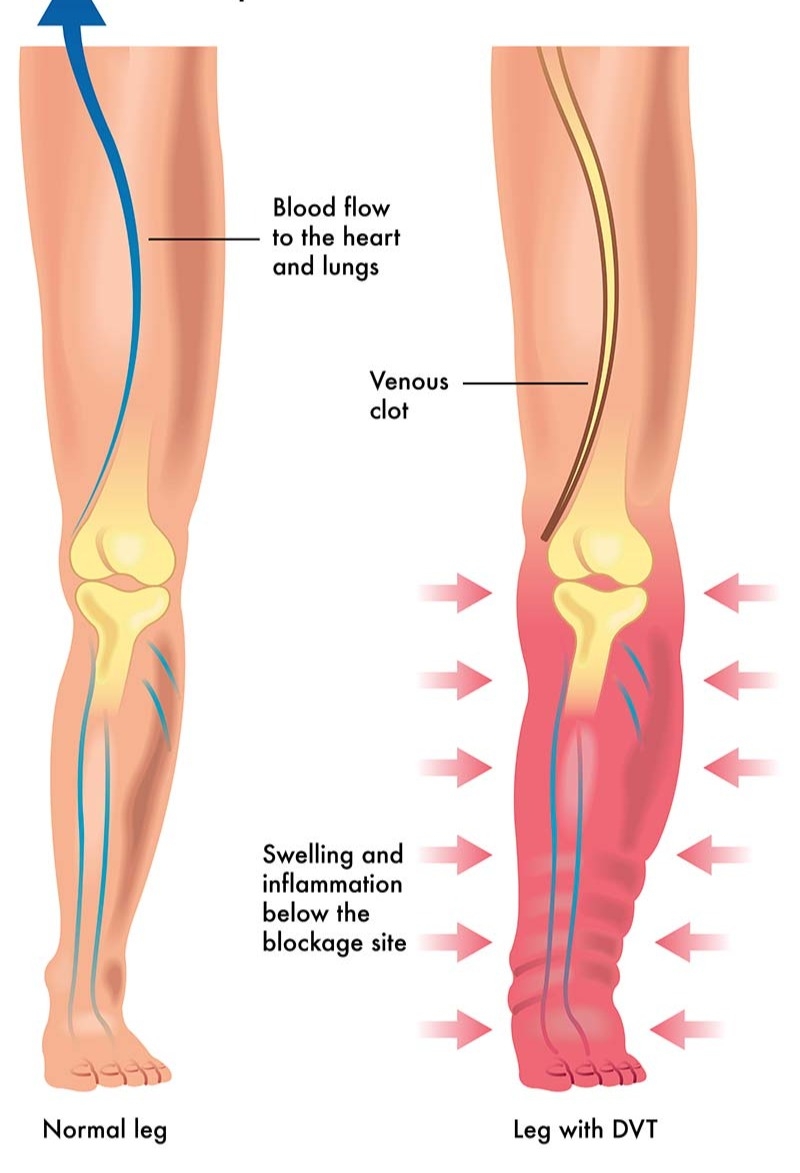
- Venous thrombosis (clotting)
- Non-thrombotic venous stenosis
- Advanced age
- Family history of venous disease
- Smoking
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Lower extremity trauma
- Prior venous thrombosis
- Pregnancy
- Symptoms: calf pain, leg heaviness and aching, swelling of the calves, muscle cramps, and skin irritation (tightness, dryness, itching)
- Clinical signs:
- Telangiectasias: dilated intradermal and subdermal veins (spider veins)
- Most prevalent clinical sign
- Varicose veins: dilated, elongated, tortuous, dilated subcutaneous veins
- >/= 3 mm in diameter
- Often concerning to patients for cosmetic reasons
- Telangiectasias: dilated intradermal and subdermal veins (spider veins)
- Signs of more advanced disease:
- Edema (swelling)
- Skin changes
- Hyperpigmentation (discoloration) and induration (hardening)
- Ulceration