Mesenteric Ischemia: What You Should Know
Mesenteric Ischemia: What You Should Know
What is Mesenteric Ischemia?
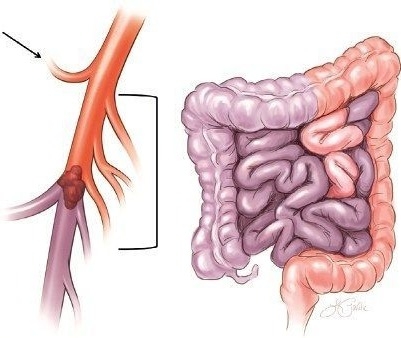
Mesenteric ischemia is a condition that occurs when blood flow to your intestines is restricted. There are three primary arteries that deliver blood to your intestines known as the mesenteric arteries. When these arteries become blocked or narrowed, your digestive tract may not be supplied with the amount of blood and oxygen it needs to function properly, which can lead to serious health complications and even death.
Symptoms of Mesenteric Ischemia
There are two types of mesenteric ischemia: acute and chronic. Acute mesenteric ischemia develops when a blood clot suddenly blocks the flow of blood to the small intestines. Chronic mesenteric ischemia develops slowly over time.
Common symptoms of acute mesenteric ischemia include:
Common symptoms of chronic mesenteric ischemia include:
If you experience severe abdominal pain that comes on suddenly, it is important to seek medical attention as quickly as possible. Likewise, if you notice abdominal pain within an hour of eating, it is best to schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider. If left untreated, both acute and chronic mesenteric ischemia can lead to uncomfortable and dangerous health complications.
Not seeking immediate medical care for acute mesenteric ischemia can lead to:
Living with chronic mesenteric ischemia can cause:
Mesenteric ischemia can happen to anyone, regardless of their age or medical history. While this is true, the condition is more common in individuals with cardiovascular disease. This is because the arteries that bring blood to your intestines come from the heart's primary artery. When plaque builds up on the inside of your arteries as a result of factors such as smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol, this can lead to both heart disease and mesenteric ischemia. Similarly, heart disease can also contribute to the formation of blood clots that result in acute mesenteric ischemia.
Treatment Options for Mesenteric Ischemia
If you are diagnosed with acute mesenteric ischemia, you will most likely have to undergo immediate surgery to remove the clot that is blocking blood flow to your intestines. If your arteries are narrowed but not totally blocked, your healthcare provider may recommend that you undergo an angioplasty and stent procedure in order to reopen your artery and allow the blood to flow properly again. Additional steps to treat mesenteric ischemia could include making lifestyle changes such as not smoking, taking antibiotics to treat infections caused by the blockage, and/or taking blood thinners to prevent future blockages.
The Vascular Institute Can Help Protect Your Arteries
While cardiovascular complications such as mesenteric ischemia may not always be preventable, there are steps you can take to keep your heart, veins, and arteries strong. The trusted team at the Vascular Institute of the Rockies is eager to help you maintain a healthy cardiovascular system for life. Visit us online today to schedule an appointment or to learn more.
Go Back What is Mesenteric Ischemia?
Mesenteric ischemia is a condition that occurs when blood flow to your intestines is restricted. There are three primary arteries that deliver blood to your intestines known as the mesenteric arteries. When these arteries become blocked or narrowed, your digestive tract may not be supplied with the amount of blood and oxygen it needs to function properly, which can lead to serious health complications and even death.
Symptoms of Mesenteric Ischemia
There are two types of mesenteric ischemia: acute and chronic. Acute mesenteric ischemia develops when a blood clot suddenly blocks the flow of blood to the small intestines. Chronic mesenteric ischemia develops slowly over time.
Common symptoms of acute mesenteric ischemia include:
- Sudden, severe abdominal pain
- Urgent need to go to the bathroom
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
Common symptoms of chronic mesenteric ischemia include:
- Abdominal pain that occurs around half an hour after eating
- Pain that gets worse within an hour
- Pain that goes away after one to three hours
If you experience severe abdominal pain that comes on suddenly, it is important to seek medical attention as quickly as possible. Likewise, if you notice abdominal pain within an hour of eating, it is best to schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider. If left untreated, both acute and chronic mesenteric ischemia can lead to uncomfortable and dangerous health complications.
Not seeking immediate medical care for acute mesenteric ischemia can lead to:
- Irreversible damage to your bowels: Parts of your bowels can die without an adequate amount of blood flow.
- Sepsis: If the lack of blood supply leads to bowel death, this could lead to a blood infection or sepsis, which could cause other organs to fail.
- Death: Complications caused by the lack of blood flow to your bowels could put your life in danger.
Living with chronic mesenteric ischemia can cause:
- Fear of eating: Because of the pain that occurs after eating, you may be afraid to eat as often or as much as you need to.
- Weight loss: Because you are afraid to eat, you could unintentionally lose weight.
- Acute-on-chronic mesenteric ischemia: The condition can progress, resulting in acute mesenteric ischemia.
Mesenteric ischemia can happen to anyone, regardless of their age or medical history. While this is true, the condition is more common in individuals with cardiovascular disease. This is because the arteries that bring blood to your intestines come from the heart's primary artery. When plaque builds up on the inside of your arteries as a result of factors such as smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol, this can lead to both heart disease and mesenteric ischemia. Similarly, heart disease can also contribute to the formation of blood clots that result in acute mesenteric ischemia.
Treatment Options for Mesenteric Ischemia
If you are diagnosed with acute mesenteric ischemia, you will most likely have to undergo immediate surgery to remove the clot that is blocking blood flow to your intestines. If your arteries are narrowed but not totally blocked, your healthcare provider may recommend that you undergo an angioplasty and stent procedure in order to reopen your artery and allow the blood to flow properly again. Additional steps to treat mesenteric ischemia could include making lifestyle changes such as not smoking, taking antibiotics to treat infections caused by the blockage, and/or taking blood thinners to prevent future blockages.
The Vascular Institute Can Help Protect Your Arteries
While cardiovascular complications such as mesenteric ischemia may not always be preventable, there are steps you can take to keep your heart, veins, and arteries strong. The trusted team at the Vascular Institute of the Rockies is eager to help you maintain a healthy cardiovascular system for life. Visit us online today to schedule an appointment or to learn more.